nema plug chart pdf
NEMA plug charts are essential for identifying plug and receptacle configurations, ensuring safety, and compliance with electrical standards. They streamline the selection process for various applications.
1.1 What is a NEMA Plug Chart?
A NEMA plug chart is a reference guide detailing standard configurations for plugs and receptacles. It provides essential information on ratings, polarity, and compatibility, ensuring safe and proper electrical connections. These charts are widely used to match plugs with receptacles, decode NEMA ratings, and verify compliance with electrical standards. They are invaluable for electricians, engineers, and DIY enthusiasts alike.
1.2 Importance of NEMA Configurations
NEMA configurations are critical for ensuring safe and efficient electrical connections. They standardize plug and receptacle designs, preventing mismatches that could cause electrical hazards. Proper configurations guarantee compatibility with specific voltage and current requirements, reducing the risk of overloads or short circuits. This standardization also simplifies installation and troubleshooting, ensuring compliance with safety regulations for both residential and industrial applications.
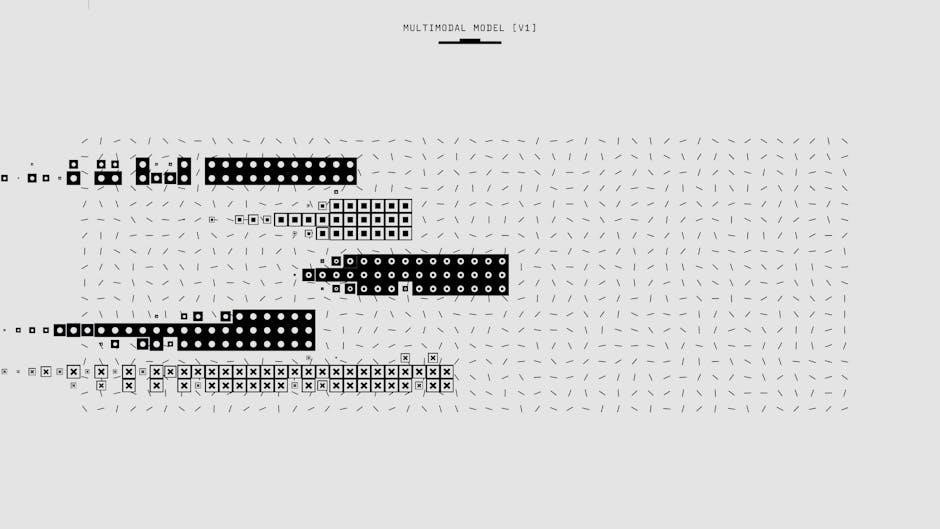
NEMA Configurations for Plugs and Receptacles
NEMA configurations standardize plug and receptacle designs, ensuring compatibility and safety. They specify voltage, current, and wiring requirements, enabling proper connections for various electrical applications and devices.
2.1 Non-Locking Plugs and Receptacles
Non-locking plugs and receptacles are commonly used for general-purpose electrical connections. They are easy to connect and disconnect, making them suitable for household and light-duty applications. These devices are rated for specific voltages and amperages, such as 15A, 20A, and 30A, ensuring safe and efficient power delivery. They are widely available and cost-effective, meeting basic electrical needs.
2.2 Locking Plugs and Receptacles
Locking plugs and receptacles provide a secure connection, ideal for high-power or industrial applications where accidental disconnection is a concern. They ensure reliability and safety in demanding environments. Available in various configurations like 20A, 30A, and multi-wire setups, they offer enhanced durability and are designed to meet specific electrical requirements, ensuring uninterrupted power supply in critical operations.

How to Read a NEMA Plug Chart
Reading a NEMA plug chart involves understanding configurations, ratings, and wiring diagrams. It helps users match plugs and receptacles correctly, ensuring compatibility and safety in electrical connections.
3.1 Decoding NEMA Ratings
Decoding NEMA ratings involves understanding the numeric and letter designations. The number indicates the maximum current in amps, while letters denote voltage and wiring configurations. For example, 5-15R signifies a 125V, 15A receptacle. This system ensures compatibility and safety by standardizing plug and receptacle connections. Proper decoding is crucial for selecting the right equipment for specific electrical requirements.
3.2 Understanding Ampere and Voltage Ratings
Ampere and voltage ratings are critical for safe connections. Amps indicate the maximum current a plug or receptacle can handle, while voltage specifies the electrical pressure. Higher amps require thicker wires to prevent overheating. Matching the correct amp and voltage ensures efficient energy transfer and avoids hazards. Always refer to the NEMA chart to align ratings with your equipment’s needs for optimal performance and safety.

Common NEMA Plug and Receptacle Ratings
Common ratings include 15A, 20A, and 30A for plugs and receptacles, with voltages ranging from 125V to 277V. These standards ensure compatibility and safety across applications.
4;1 15 AMP, 20 AMP, and 30 AMP Ratings
15 AMP, 20 AMP, and 30 AMP ratings are standard for NEMA plugs and receptacles. These ratings indicate the maximum current a device can safely handle. A 15 AMP plug is suitable for lightweight appliances, while 20 AMP and 30 AMP plugs are designed for higher power demands, such as heavy machinery or industrial equipment. Proper matching ensures electrical safety and efficiency.
4.2 125V, 250V, and 277V Configurations
125V, 250V, and 277V configurations are standardized for NEMA plugs and receptacles. 125V is common in residential and light commercial use, while 250V is often used for heavy-duty applications. 277V configurations are typically found in industrial settings for high-power equipment. These voltage ratings ensure compatibility and safety, preventing overloading and electrical hazards when matched correctly with the appropriate devices and systems.
Differences Between Plugs and Receptacles
Plugs (male) and receptacles (female) differ in their roles. Plugs initiate connections, while receptacles receive them, ensuring safe and proper electrical circuit functionality.
5.1 Plug (P) vs. Receptacle (R)
NEMA plugs (P) are male connectors with prongs that insert into receptacles (R), which are female outlets. Plugs initiate the electrical connection, while receptacles provide the socket for insertion. The “P” denotes a plug, and “R” signifies a receptacle, ensuring compatibility and safe electrical connections. This distinction is crucial for proper mating and functionality in any electrical system.
5.2 Male vs. Female Configurations
In NEMA configurations, male connectors are characterized by protruding prongs (plugs), while female connectors feature recessed slots (receptacles). This distinction ensures secure, foolproof connections, preventing mismating. Male plugs initiate the connection, while female receptacles provide the socket for insertion, maintaining electrical continuity and safety. This gender-based design is fundamental to NEMA standards, ensuring compatibility and efficient power delivery across applications.
Wiring Diagrams for NEMA Plugs
NEMA wiring diagrams provide detailed layouts for plug configurations, showcasing prong arrangements and wire connections. They guide installations, ensuring proper electrical connections and safety standards are met.
6.1 Straight Blade Plugs
Straight blade plugs are non-locking connectors with flat prongs, commonly used in household and light-duty applications. They are available in various configurations, such as 15A, 20A, and 30A ratings, and operate at 125V or 250V. The wiring diagrams for these plugs typically show two or three prongs, with clear markings for hot, neutral, and ground wires. Proper wiring ensures safe and efficient power delivery, adhering to NEMA standards. These diagrams are essential for installers to avoid mismatches and ensure compliance with electrical codes, guaranteeing reliable performance and safety in all applications.
6.2 Locking Plugs
Locking plugs provide a secure, twist-lock connection, ideal for industrial and heavy-duty applications. They come in 20A/30A configurations and are available with 3, 4, or 5 wires. Wiring diagrams for locking plugs highlight the importance of proper connections to ensure safe and reliable power delivery. These plugs are designed to prevent accidental disconnection, making them suitable for high-power equipment and harsh environments. Always refer to NEMA standards for correct installation and safety compliance.

Applications of NEMA Plugs and Receptacles
NEMA plugs and receptacles are used across industrial, commercial, and residential environments for powering equipment, appliances, and devices. They are essential for heavy machinery, high-power tools, and specialized applications like data centers and outdoor events, ensuring reliable electrical connections and safety.
7.1 Industrial Applications
NEMA plugs and receptacles are extensively used in industrial settings for high-power machinery and equipment. They provide secure connections for motors, pumps, and automation systems, ensuring reliable operation in demanding environments. Industrial applications often require higher amperage and voltage ratings, making NEMA configurations essential for maintaining efficiency and safety in manufacturing and processing facilities;
7.2 Commercial and Residential Use
NEMA plugs and receptacles are widely used in commercial and residential settings for powering appliances and devices. They provide standardized connections for lighting, HVAC systems, and household equipment. Common configurations like 15-20 AMP and 125-250V ratings ensure compatibility and safety for everyday use. Residential applications often rely on 5-15R and 5-20R receptacles, while commercial settings may require higher-rated options like 6-50R for heavy-duty equipment.

Safety Standards and Compliance
NEMA plug charts ensure compliance with ANSI and NEMA safety standards, emphasizing proper grounding and polarization to prevent electrical hazards in residential and commercial applications.
8.1 ANSI and NEMA Safety Regulations
ANSI and NEMA safety regulations ensure electrical devices meet rigorous standards for performance, safety, and compatibility. These regulations mandate proper grounding, polarization, and voltage ratings to prevent hazards. Compliance with these standards is critical for avoiding electrical risks in both residential and industrial settings, ensuring reliable and safe connections for all NEMA-rated plugs and receptacles.
8.2 Grounding and Polarization Requirements
Grounding and polarization are critical for safe electrical connections. Grounding provides a path for excess current, preventing shocks, while polarization ensures proper voltage and current flow direction. NEMA plug charts detail these requirements, emphasizing configurations like 3-pole 4-wire grounding and 2-pole 2-wire setups. These standards ensure compliance with safety protocols and prevent electrical hazards in various applications.

How to Use a NEMA Plug Chart
NEMA plug charts simplify selecting the right plug or receptacle by matching configurations, amp ratings, and voltage requirements, ensuring safe and compatible electrical connections for any application.
9.1 Matching Plugs to Receptacles
Using a NEMA plug chart, identify the receptacle type by its configuration and rating. Ensure the plug matches the receptacle’s voltage, amperage, and wiring layout to guarantee compatibility and safety. Cross-reference the chart to avoid mismatches, which can cause electrical hazards. Proper alignment of poles, wires, and grounding ensures efficient and safe power delivery to connected devices, preventing potential damage or risks.
9.2 Determining the Correct Configuration
Refer to the NEMA plug chart to determine the correct configuration by verifying voltage, amperage, and wiring requirements. Match the device’s specifications with the chart’s details, ensuring alignment of poles, wires, and grounding. This step is crucial for safe and efficient electrical connections, preventing mismatches that could lead to hazards or equipment damage. Always cross-check ratings and configurations to ensure compatibility.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Common mistakes include mismatching ampere ratings, incorrect voltage selection, and ignoring grounding requirements. Always verify NEMA configurations to ensure compatibility and safety in electrical connections.
10.1 Mismatching Ampere Ratings
Mismatching ampere ratings is a critical error that can lead to overheating, fire hazards, or equipment damage. Always ensure the plug and receptacle ampere ratings match the device’s requirements. Using a higher or lower ampere configuration can cause electrical instability or safety risks. Refer to the NEMA chart to verify compatibility and avoid such dangerous mismatches in your electrical setup.
10.2 Incorrect Voltage Selection
Incorrect voltage selection can lead to equipment damage, electrical fires, or unsafe operating conditions. Always verify the voltage requirements of your device and match them with the appropriate NEMA plug or receptacle configuration. Using a plug or receptacle rated for the wrong voltage can result in malfunction or hazards. Refer to the NEMA chart to ensure proper voltage compatibility and maintain electrical safety standards.
Locking Plugs and Receptacles
Locking plugs and receptacles provide secure connections, preventing accidental disconnections. Common configurations include 20A and 30A options with 3, 4, or 5 wires. They are ideal for industrial environments requiring high reliability and safety.
11.1 20A/30A Locking Configurations
20A and 30A locking configurations are commonly used in industrial settings for high-power applications. These plugs and receptacles ensure secure connections, preventing accidental disconnections. They are available in various wire configurations, including 3, 4, or 5 wires, and are rated for 125/250V or 277V. Their robust design ensures durability and compliance with safety standards, making them ideal for demanding environments.
11.2 3, 4, and 5 Wire Locking Plugs
3, 4, and 5 wire locking plugs offer versatility for various electrical needs. The 3-wire configuration is ideal for single-phase applications with grounding, while 4-wire plugs support three-phase power with a ground. 5-wire plugs add an extra contact for control or signaling. These configurations ensure reliable connections in industrial and high-power settings, adhering to NEMA and ANSI safety standards for secure and efficient operation.
NEMA plug charts are vital tools for ensuring safe and efficient electrical connections. They provide clarity on configurations, ratings, and compliance, helping users make informed decisions.
12.1 Summary of Key Points
NEMA plug charts provide a comprehensive guide to plug and receptacle configurations, ensuring compatibility and compliance. They detail ampere, voltage, and wiring requirements, as well as locking and non-locking types. These charts are essential for selecting the correct plug or receptacle for specific applications, ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical systems. Proper use prevents mismatches and hazards.
12.2 Final Tips for Using NEMA Charts
Always match plugs to receptacles using NEMA charts to ensure compatibility and safety. Verify ampere and voltage ratings to avoid mismatches. Consult the chart before ordering to confirm configurations. Understand the difference between locking and non-locking plugs for specific applications. Refer to manufacturer guides for detailed wiring diagrams and safety standards. Regularly update your charts to comply with the latest NEMA specifications;
Resources for Further Reading
Visit official NEMA websites and manufacturer sites like Qualtek for printable PDF charts, detailed guides, and updated specifications on plugs and receptacles.
13.1 Printable NEMA Plug Charts
Downloadable PDF charts from manufacturers like Qualtek offer detailed configurations for plugs and receptacles, including amp and voltage ratings. These charts are ideal for quick reference and installation guides, ensuring compliance with NEMA standards and simplifying electrical setup processes for both residential and industrial applications.
13.2 Manufacturer Websites and Guides
Manufacturer websites, such as Qualtek and Hubbell, provide comprehensive guides and charts for NEMA plugs and receptacles. These resources include detailed wiring diagrams, configuration charts, and technical specifications, ensuring users can accurately match plugs to receptacles. They also offer FAQs and user manuals, making it easier to understand and apply NEMA standards effectively in various electrical applications.
